The Transformative Power of Smartphones: A Comprehensive Analysis with Real-World Cases and Innovative Solutions
The advent of smartphones marks one of the most significant technological revolutions in recent history. These pocket-sized computers, equipped with advanced computing capabilities, internet connectivity, and a plethora of applications, have become indispensable for billions worldwide. From facilitating instant communication to enabling complex financial transactions, smartphones have democratized access to information and services, fostering a more interconnected and efficient society. However, this rapid proliferation also presents challenges, including digital divides, privacy concerns, and addiction issues. This paper delves into these aspects, highlighting success stories and proposing practical solutions to harness the full potential of smartphones while mitigating their drawbacks.
Technological Advancements and Features
Smartphones today are marvels of engineering, integrating high-resolution displays, powerful processors, sophisticated cameras, and advanced operating systems. The introduction of 5G technology, for instance, promises ultra-fast internet speeds, enabling real-time video conferencing, seamless streaming, and the development of emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). Features such as biometric authentication (fingerprint/face recognition) and secure payments have enhanced user security and convenience.
Case Study 1: Mobile Health (mHealth) in Rural India
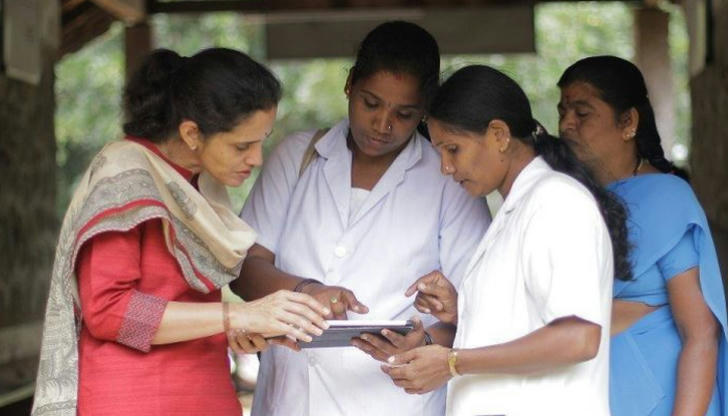
Background: In rural India, access to healthcare services is limited due to geographical barriers and a shortage of medical professionals. The introduction of mHealth apps and services has transformed the landscape, leveraging smartphones to bridge this gap. Implementation: One notable example is the "mDiabetes" app developed by a collaboration between a tech startup and local health authorities. The app enables patients with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels, receive personalized diet and exercise advice, and consult with doctors remotely. It also provides health workers with data analytics tools to track patient progress and identify at-risk individuals. Outcomes: The results have been remarkable, with significant improvements in glycemic control among users and a reduction in complications related to diabetes. This initiative has not only improved health outcomes but also alleviated the burden on overstretched healthcare resources.

Solution Proposed: To further enhance mHealth services, governments and private sectors should invest in infrastructure upgrades, such as expanding mobile network coverage and establishing telehealth hubs in rural areas. Additionally, promoting digital literacy among healthcare workers and patients is crucial to ensure effective utilization of these tools.
Case Study 2: Digital Education in Sub-Saharan Africa
Background: Education in many parts of Sub-Saharan Africa is hindered by a lack of resources, including textbooks, teachers, and classrooms. Smartphones offer a promising solution to this crisis by providing a platform for digital learning. Implementation: Organizations like One Laptop per Child (OLPC) and local educational startups have developed apps that deliver interactive lessons, quizzes, and educational videos to students' smartphones. These apps often work offline, catering to regions with limited internet connectivity. They cover a wide range of subjects, from basic literacy and numeracy to science and technology. Outcomes: Studies have shown significant improvements in learning outcomes, with students demonstrating higher engagement and retention rates compared to traditional teaching methods. Moreover, smartphones have democratized access to education, allowing children from remote and underserved communities to learn at their own pace. Solution Proposed: To scale up digital education initiatives, international cooperation is essential. Donor agencies and governments should fund the development and distribution of educational apps, while also investing in solar-powered charging stations to address the issue of electricity scarcity. Collaboration with local content creators to develop culturally relevant and linguistically diverse educational materials is also vital. Economic Implications and Digital Divide Smartphones have been a catalyst for economic growth, enabling entrepreneurship, facilitating e-commerce, and enhancing productivity across sectors. However, the digital divide, where access to technology is unequal based on socio-economic status, geography, or age, threatens to exacerbate existing inequalities.
Case Study 3: E-Commerce Boom in Southeast Asia
Background: Southeast Asia has experienced an e-commerce explosion, driven largely by smartphone adoption. Platforms like Shopee, Lazada, and GoJek have transformed how people shop, pay, and even work. Implementation: These platforms offer a seamless shopping experience, integrating payment systems, logistics, and customer service into a single app. They have empowered small businesses to reach wider markets and created new job opportunities, particularly for youth and women. Outcomes: The economic impact has been substantial, with e-commerce contributing significantly to GDP growth in countries like Indonesia and Vietnam. It has also fostered financial inclusion by providing easy access to digital payments and credit services.

Solution Proposed: To ensure equitable benefits from e-commerce growth, governments should implement policies that support digital literacy programs, provide subsidies for smartphones and internet access to low-income families, and encourage the development of local e-commerce platforms. This will help bridge the digital divide and promote inclusive economic growth. Privacy and Security Concerns As smartphones become more integrated into our lives, concerns about data privacy and cybersecurity escalate. Personal information, from location data to financial transactions, is stored on these devices, making them targets for hackers and state surveillance.
Case Study 4: Data Protection in Europe
Background: The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a landmark legislation aimed at protecting individuals' privacy and personal data. It sets strict guidelines for how companies collect, store, and process data. Implementation: GDPR requires businesses to obtain explicit consent for data collection, provide users with the right to be forgotten (data deletion), and implement robust security measures to safeguard data. Outcomes: Since its implementation, GDPR has raised awareness about data privacy rights and prompted companies worldwide to review and strengthen their data protection policies. It has also led to significant fines for companies that violate these regulations, serving as a deterrent. Solution Proposed: Globally, there is a need for similar comprehensive data protection laws. International cooperation and standardization of data protection regulations can help create a safer digital environment. Additionally, users must be educated about safe browsing practices, the importance of strong passwords, and the use of encryption tools. Smartphone Addiction and Mental Health The ubiquity of smartphones has led to concerns about addiction and its impact on mental health, particularly among adolescents. Excessive screen time has been linked to sleep disturbances, anxiety, and depression.
Case Study 5: Digital Wellbeing Features
Background: Recognizing the potential harm, smartphone manufacturers have introduced digital wellbeing features aimed at promoting healthier usage habits. Implementation: Features such as screen time trackers, app usage limits, and do-not-disturb modes are now standard on most smartphones. Apple's "Screen Time" and Google's "Digital Wellbeing" tools provide users with insights into their device usage patterns and allow them to set boundaries. Outcomes: While these features are a step in the right direction, their effectiveness depends on user awareness and willingness to adopt them. Studies suggest that awareness alone can lead to a reduction in screen time and improved mental health outcomes. Solution Proposed: A multi-faceted approach is necessary to address smartphone addiction. This includes integrating digital wellbeing education into school curricula, encouraging family discussions about healthy technology use, and developing more sophisticated algorithms that can detect and intervene when addictive patterns are identified.
Conclusion
Smartphones have undeniably revolutionized our world, offering unprecedented access to information, services, and opportunities. However, their transformative power also brings challenges that must be addressed through innovative solutions and collaborative efforts. By leveraging real-world cases and best practices, this paper has illustrated how smartphones can be harnessed to drive positive change across various sectors while mitigating potential harms. As we continue to navigate this digital age, it is crucial to strike a balance between embracing technological advancements and safeguarding our societal well-being.
