The Evolution and Benefits of Laser Eye Surgery: A Breakthrough in Vision Correction
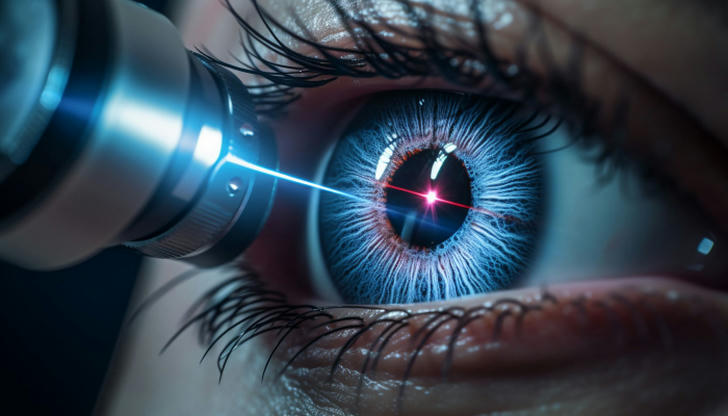

Laser eye surgery, also known as refractive surgery, has become a widely accepted and highly effective solution for individuals who suffer from refractive vision problems such as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), and astigmatism. The procedure involves the use of focused laser beams to reshape the cornea of the eye, allowing light entering the eye to be properly focused onto the retina. This breakthrough in vision correction has transformed the lives of millions, providing them with clearer, sharper vision without the need for glasses or contact lenses. This essay delves into the history and development of laser eye surgery, explains the various types of procedures, highlights the benefits and risks, and examines its future potential.
The History and Development of Laser Eye Surgery
Laser eye surgery was not an immediate breakthrough but the result of years of innovation and refinement. The history of laser technology in ophthalmology dates back to the early 1980s, when scientists began experimenting with lasers as a tool for vision correction. However, the groundwork for modern laser eye surgery can be traced to earlier procedures that used more conventional techniques, such as radial keratotomy (RK) in the 1970s, which aimed to correct nearsightedness by making small incisions in the cornea. In the early 1980s, two key developments made laser eye surgery a viable option for vision correction: 1.The Introduction of the Excimer Laser: The excimer laser, developed in 1983, became the cornerstone of laser eye surgery. Unlike other lasers, excimer lasers can emit ultraviolet light with precision, allowing the cornea to be reshaped without causing heat damage to surrounding tissues. This laser was initially used in industrial applications but found its place in ophthalmology as it could precisely remove corneal tissue. 2.The Development of LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis): LASIK, developed in the 1990s, is the most popular laser eye surgery procedure today. It combines two lasers: the first one is used to create a thin flap on the cornea, and the second reshapes the cornea underneath. LASIK revolutionized the field because it improved recovery times and minimized discomfort compared to earlier procedures. 3.Following LASIK, other advanced techniques, such as PRK (photorefractive keratectomy) and SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction), were introduced, each offering unique advantages for different types of patients and conditions.
Types of Laser Eye Surgery Procedures
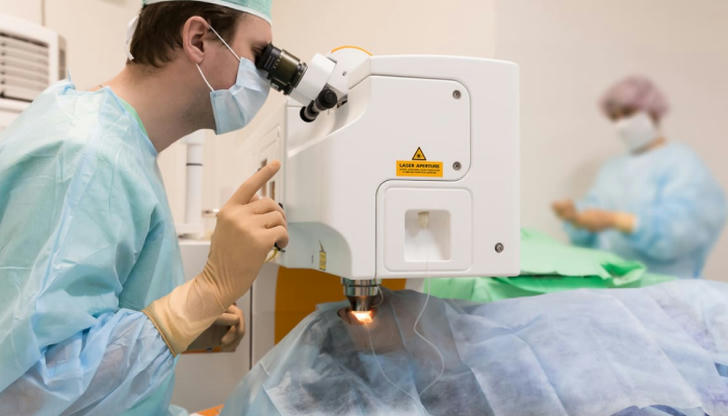
While LASIK is the most commonly performed procedure, there are several types of laser eye surgeries available today, each tailored to the needs of different patients.
- LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) LASIK has become the gold standard for laser eye surgery due to its high success rate and relatively quick recovery time. The procedure involves three main steps: Flap Creation: The surgeon uses a laser or a microkeratome (a precision surgical instrument) to create a thin flap in the cornea. Corneal Reshaping: The excimer laser is then used to reshape the underlying corneal tissue by removing tiny amounts of tissue. This correction helps to focus light properly on the retina, improving vision. Flap Replacement: After reshaping, the corneal flap is placed back in its original position where it naturally adheres without the need for stitches. One of the key advantages of LASIK is the rapid recovery time. Most patients experience significant improvement in vision within a day or two after the procedure, and the risk of complications is relatively low.
- PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy) PRK is similar to LASIK in that it uses a laser to reshape the cornea, but the procedure differs in how the cornea is prepared. In PRK, the outer layer of the cornea (the epithelium) is completely removed before the laser is used to reshape the underlying corneal tissue. Afterward, the epithelium regenerates naturally over a few days. While PRK has a longer recovery period than LASIK, it may be a better option for individuals with thinner corneas or those who are not good candidates for LASIK due to factors such as dry eyes or high refractive error.
- SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction) SMILE is a newer, minimally invasive procedure that uses a femtosecond laser to create a small disc-shaped piece of corneal tissue (lenticule) beneath the surface. This lenticule is then removed through a small incision, reshaping the cornea and improving the focus of light entering the eye. SMILE offers several advantages over LASIK and PRK, including: •No corneal flap creation: Since SMILE doesn’t involve creating a flap, there is less risk of complications related to flap healing. •Minimally invasive: The small incision required in SMILE results in less disruption to the corneal nerves, which reduces the risk of dry eyes. •Faster recovery: While SMILE may not have quite the same rapid visual improvement as LASIK, many patients experience less discomfort and quicker healing than with PRK.
- LASEK (Laser-Assisted Subepithelial Keratomileusis) LASEK is similar to PRK but differs in the method of removing the epithelial layer. In LASEK, an alcohol solution is used to loosen the epithelium, which is then pushed aside. After the laser reshapes the cornea, the epithelial layer is repositioned. This procedure offers an alternative for patients with thin corneas but has a slightly longer recovery time than LASIK.
Benefits of Laser Eye Surgery

Laser eye surgery has transformed the landscape of vision correction, providing numerous benefits to patients. Below are some of the primary advantages:
- Improved Vision The most significant benefit of laser eye surgery is the improvement in vision. Most patients experience a dramatic reduction or complete elimination of their dependence on glasses or contact lenses. The goal of the surgery is to correct the underlying refractive error and provide clearer, sharper vision at all distances.
- Quick and Painless Procedure The procedure is generally quick, lasting only about 10-15 minutes per eye. It is typically performed on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can go home the same day. Local anesthesia in the form of eye drops is used to numb the eyes, and patients report minimal discomfort during the surgery. After the procedure, there may be some mild irritation or dryness, but these symptoms typically subside within a few days.
- Long-Term Results One of the key reasons for the popularity of laser eye surgery is its long-lasting results. Most patients experience stable vision for many years following the procedure. Unlike other vision correction methods, such as glasses or contact lenses, which need to be replaced periodically, laser eye surgery offers a permanent solution to refractive errors.
- Quick Recovery and Minimal Downtime Recovery time for most laser eye surgeries is minimal. Patients undergoing LASIK typically experience improved vision within a day, and while it may take a few weeks for the full benefits to be realized, most individuals are able to return to their normal activities, including driving and working, within a few days. For PRK and SMILE, the recovery period may be slightly longer, but the discomfort is typically manageable.
- Reduced Risk of Eye Infections For those who wear contact lenses, there is always a risk of eye infections due to improper lens care or wearing lenses for too long. Laser eye surgery eliminates the need for contact lenses, thus reducing the risk of infection and irritation caused by wearing contacts.
Risks and Considerations

While laser eye surgery has a high success rate and offers numerous benefits, it is not without its risks. Some of the potential risks and complications include: •Dry Eyes: Temporary dry eyes are common after the surgery, and in some cases, patients may experience prolonged dryness. •Undercorrection or Overcorrection: In some cases, the laser may not remove enough tissue or may remove too much, resulting in undercorrection or overcorrection. Additional procedures or enhancements may be necessary to achieve optimal vision. •Night Vision Issues: Some patients may experience glare, halos, or difficulty seeing at night, especially after LASIK. This typically resolves over time but can be a concern for some individuals. •Complications from the Flap (LASIK): In LASIK, complications related to the corneal flap, such as dislocation or infection, can occur, although these complications are rare. Candidates for laser eye surgery need to meet certain health criteria, such as having a stable prescription and being free from conditions like severe dry eye or corneal disease.
The Future of Laser Eye Surgery
The future of laser eye surgery is promising, with continual advancements in laser technology, surgical techniques, and personalized treatment plans. Some of the key developments to watch for include: •Custom Wavefront Technology: This advanced technology creates a detailed map of the eye to tailor the laser treatment to each patient’s unique corneal structure. This approach can improve the accuracy of the surgery and reduce the risk of complications. •Smarter Lasers: Future lasers will likely have even greater precision and the ability to target specific problem areas in the cornea with greater accuracy, offering even better results. •Treatment for Presbyopia: Although laser eye surgery is already effective for treating refractive errors like myopia and hyperopia, it has yet to offer a full solution for age-related presbyopia (the inability to focus on close objects). However, research is ongoing, and innovations in laser technology may soon provide a solution.
Conclusion
Laser eye surgery has revolutionized the field of vision correction, providing a safe, effective, and lasting solution for those seeking to eliminate their dependence on glasses and contact lenses. With a variety of procedures available, patients can choose the one that best suits their needs, resulting in clearer vision, a faster recovery, and improved quality of life. As technology continues to advance, the future of laser eye surgery looks even brighter, offering patients even greater precision and enhanced outcomes. Whether improving the everyday quality of life or helping patients with more complex vision issues, laser eye surgery remains one of the most significant breakthroughs in modern medicine.
