Injectable Weight Loss Treatments: An Overview of Effectiveness, Risks, and Future Trends

The global rise in obesity has led to an increasing demand for weight loss solutions. While diet and exercise remain the cornerstone of weight management, more people are turning to medical treatments to help accelerate fat loss, especially for those struggling with significant weight gain. Among the most talked-about treatments are injectable weight loss therapies, which promise quick results with minimal effort. These treatments are designed to suppress appetite, increase fat metabolism, or alter the body’s ability to store fat. Popular options like lipotropic injections, GLP-1 agonists, and B12 shots have grown in popularity in recent years, promising quick and effective results. However, despite their allure, the effectiveness, safety, and long-term benefits of these injections are subjects of ongoing research and debate. This article will provide an overview of injectable weight loss treatments, including their types, mechanisms of action, potential benefits, risks, and what the future holds for these increasingly popular medical interventions.
Types of Injectable Weight Loss Treatments
Several types of injectable treatments are available for weight loss, each with a different mechanism of action. These injections typically require administration under the skin (subcutaneously) or into the muscle (intramuscular), often provided by healthcare professionals. Some of the most common injectable weight loss treatments include lipotropic injections, GLP-1 agonists, HCG injections, and B12 shots.
- Lipotropic Injections Lipotropic injections are among the most commonly used injections for weight loss. These shots typically contain a combination of vitamins and amino acids that are believed to support the body's fat metabolism and promote fat loss. The primary ingredients often include methionine, inositol, choline, and B vitamins (such as B12), which are thought to help the liver process and remove fat more effectively. The theory behind lipotropic injections is that the ingredients support liver health, helping the body metabolize fat more efficiently and prevent fat accumulation. However, scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of lipotropic injections for weight loss is limited. While some individuals report feeling increased energy and slight weight loss, studies are inconclusive on whether these injections significantly accelerate fat loss beyond what can be achieved through diet and exercise.
- GLP-1 Agonists (e.g., Semaglutide) GLP-1 agonists, such as semaglutide (marketed as Wegovy or Ozempic), have become one of the most widely prescribed injectable treatments for weight loss. GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) is a naturally occurring hormone that helps regulate blood sugar and appetite. These drugs mimic the effects of GLP-1 in the body, resulting in several benefits for weight management: •Appetite suppression: GLP-1 agonists help reduce hunger by slowing gastric emptying and increasing satiety. •Improved insulin sensitivity: These medications also improve insulin function, which can lead to better blood sugar control and reduced fat storage. •Fat reduction: Clinical trials have shown that GLP-1 agonists can lead to significant weight loss, with some studies demonstrating up to 15% weight reduction in patients using semaglutide over a 68-week period. GLP-1 agonists are effective and have been proven to help patients lose a significant amount of weight, but they are not a quick fix. The injections need to be administered regularly (typically once a week) and should be combined with a healthy diet and exercise plan to achieve the best results.
- HCG Injections Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone that plays a key role in pregnancy. Some proponents of HCG injections claim that they can promote rapid weight loss by suppressing appetite and promoting fat metabolism. The HCG diet was originally popularized in the 1950s by Dr. Albert Simeons, who suggested that low-dose HCG combined with a very low-calorie diet (VLCD) could lead to significant weight loss. However, HCG’s effectiveness as a weight loss aid is highly controversial. While some people report initial weight loss, it is mostly attributed to the very low-calorie intake rather than the hormone itself. The FDA has explicitly stated that there is no substantial evidence to support the use of HCG for weight loss, and its use in over-the-counter weight loss treatments is illegal in many countries.
- B12 Shots Vitamin B12 injections are often used for weight loss as a part of an energy-boosting regimen. Vitamin B12 plays a critical role in energy production, red blood cell formation, and brain function. Some believe that B12 shots can boost metabolism and increase energy, helping individuals perform better during workouts or reduce the fatigue often associated with dieting. However, while vitamin B12 injections may be beneficial for individuals with a vitamin B12 deficiency, there is limited evidence to suggest that they lead to significant weight loss in individuals with normal levels of the vitamin. B12 shots can be effective for improving energy levels, which may indirectly help with exercise and overall well-being, but they should not be considered a primary method of weight loss.
How Do Injectable Weight Loss Treatments Work?

The primary mechanisms of action behind most injectable weight loss treatments revolve around altering the body's natural processes related to hunger, metabolism, and fat storage. Below are the key ways these treatments work: •Appetite Suppression: Many injectable treatments, especially GLP-1 agonists, work by reducing hunger signals to the brain. This makes individuals feel full more quickly and less inclined to overeat. •Increased Fat Metabolism: Lipotropic injections and B12 shots aim to improve the body’s ability to break down fat and use it for energy. These treatments may support liver function or increase overall metabolic rates. •Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Some injectable treatments help improve the body’s response to insulin, making it easier to control blood sugar levels and reduce fat storage. GLP-1 agonists are an example of medications that target this pathway. •Thermogenesis and Fat Burning: In some cases, injectable treatments can increase thermogenesis, the process by which the body generates heat by burning fat. This can result in greater energy expenditure and fat loss.
Effectiveness of Injectable Weight Loss Treatments
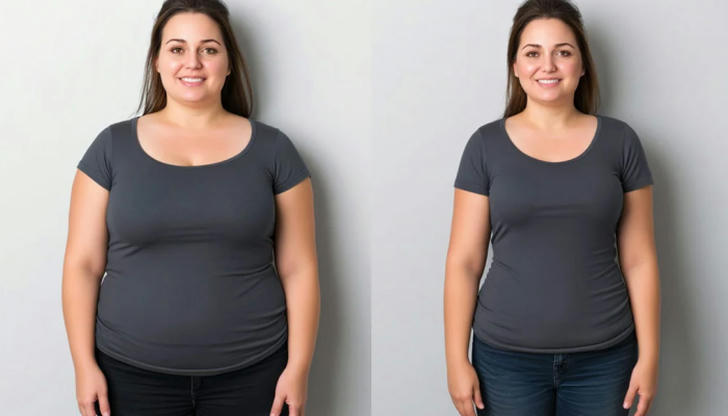

The effectiveness of injectable weight loss treatments varies depending on the type of injection and the individual’s response to it. For example: •GLP-1 agonists, such as semaglutide, have shown significant efficacy in clinical trials, with patients losing an average of 15% of their body weight over the course of a year. This makes them one of the most effective injectable treatments available for weight loss. •Lipotropic injections and B12 shots may have less evidence supporting their use for weight loss, and while they can boost energy levels and support overall health, they are unlikely to lead to significant weight loss without complementary lifestyle changes. HCG injections, despite their popularity, are not supported by substantial scientific evidence and are generally considered ineffective for weight loss by the medical community.
Risks and Side Effects of Injectable Weight Loss Treatments
While injectable weight loss treatments may offer significant benefits, they are not without risks. The potential side effects and risks of these treatments vary depending on the type of injection: •GLP-1 Agonists: These medications are generally well-tolerated but may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In some rare cases, they have been associated with more severe complications such as pancreatitis or thyroid cancer. Patients should be monitored closely by a healthcare professional. •Lipotropic Injections: While these are typically considered safe, some people may experience irritation at the injection site or allergic reactions. The benefits are also minimal for weight loss, which can lead to frustration for patients. •B12 Shots: These injections are generally considered safe, especially for individuals with a B12 deficiency. However, excessive use of B12 injections can lead to complications such as dizziness, headaches, or an allergic reaction. •HCG Injections: Since the effectiveness of HCG for weight loss is disputed, it is also associated with risks like headaches, fatigue, and possible hormone imbalances. Moreover, following the extreme low-calorie diet required with HCG injections can lead to nutritional deficiencies and other health concerns.
The Future of Injectable Weight Loss Treatments
The field of injectable weight loss treatments is rapidly evolving, with new medications and techniques continually being developed. Semaglutide, for instance, has emerged as a promising option for long-term weight management, and its growing popularity suggests that more advanced GLP-1 agonists may be developed to offer even more precise weight loss benefits. Furthermore, injectable treatments may become even more personalized in the future. Advances in genomics and precision medicine could lead to customized weight loss therapies tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup, making treatments more effective and safer. In addition, combination therapies that pair injectable treatments with diet, exercise, and other medical interventions could enhance the long-term success of weight loss programs. These therapies may include the combination of appetite suppressants with fat-burning agents or insulin-sensitizing drugs, optimizing outcomes for individuals struggling with obesity.
Conclusion
Injectable weight loss treatments offer a convenient and often effective solution for individuals seeking to manage their weight, particularly when combined with lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Treatments like GLP-1 agonists have shown significant promise in clinical trials, while other injections such as lipotropic shots and B12 injections may provide additional benefits, particularly for those looking to boost energy or improve overall metabolic health. While these treatments hold significant potential, it is essential to be aware of the risks, side effects, and the fact that weight loss is most effective when supported by long-term lifestyle changes. The future of injectable weight loss treatments looks promising, with ongoing advancements that may offer even greater results and fewer side effects. However, as with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure the right treatment plan is chosen for individual needs.
